Normally, our heart rhythm is controlled from the “sinus node”, which is located at the top of the right atrium. However, many of us have occasional heart beats that start in other areas of the heart. If the heart beat starts in the heart chambers, we call it ventricular extrasystoles. If they start in the atria, they are called “atrial extrasystoles”.
The extra beats can make it feel as though your heart has “skipped a beat”. This is because the extra beat comes so shortly after the previous normal heart beat that the heart has not had time to fill with blood – and thus the pulse becomes very weak and may not be felt at all.
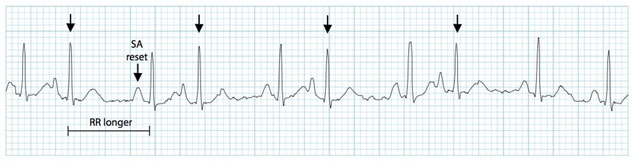
On the other hand, the pulse beat that comes after the extra beat will often feel stronger than normal. This is because the heart has had time to fill up with more blood than normal, and therefore sends the blood out into the body with a stronger pulse wave than usual.
The extra beats, in themselves, do not hurt the heart. However, they can be very bothersome and, especially if there are many of them, can increase your risk of developing atrial fibrillation. Extra beats from the atria do not increase the risk of blood clots – only atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter does.
Treatment of atrial extrasystoles
If you are bothered by the extra beats, you can try treatment. Beta-blockers, such as metoprolol succinate, bisoprolol, or atenolol will often be the first choice. You can also try calcium blockers like verapamil. If this doesn’t work, you can sometimes choose to try other drugs, such as flecainide or Tambocor. This approach requires a few days of hospitalization, during which the heart rhythm is monitored.
If it can be probable that the extra beats mainly come from the same area of the atria – in the right or left atrium – it is also possible to use ablation treatment. To do this an ECG is needed to determine where the extra strokes originate from.
If it turns out that the extra beats come from many different areas of the atria, ablation is not an option. Then one must try to solve the problem with medical treatment. This may be the case if there are other chronic strains of the heart, for example severe lung disease or significant heart valve disease.