Atrial fibrillation is triggered by excess electrical impulses, called extrasystoles. These pulses almost always come from the area of the heart where the blood vessels from the lungs, called pulmonary veins, enter the left atrium. The heart tissue in these areas is particularly predisposed to the type of problems that typically trigger atrial fibrillation. They may, however, also originate from other structures in the heart as the superior vena cava or the coronary sinus, but this is rare.
How is the treatment performed?
When doctor’s perform an ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, they heat the tissue around these problematic areas. This heating causes a scar to form, which acts as a barrier to the spread of electrical impulses. If you can heat the tissue around the entire problem area, it makes it possible to trap all the problematic electrical impulses. This prevents them from disturbing your normal heart rhythm, known as sinus rhythm. It is also the reason that ablation is sometimes called pulmonary vein isolation.
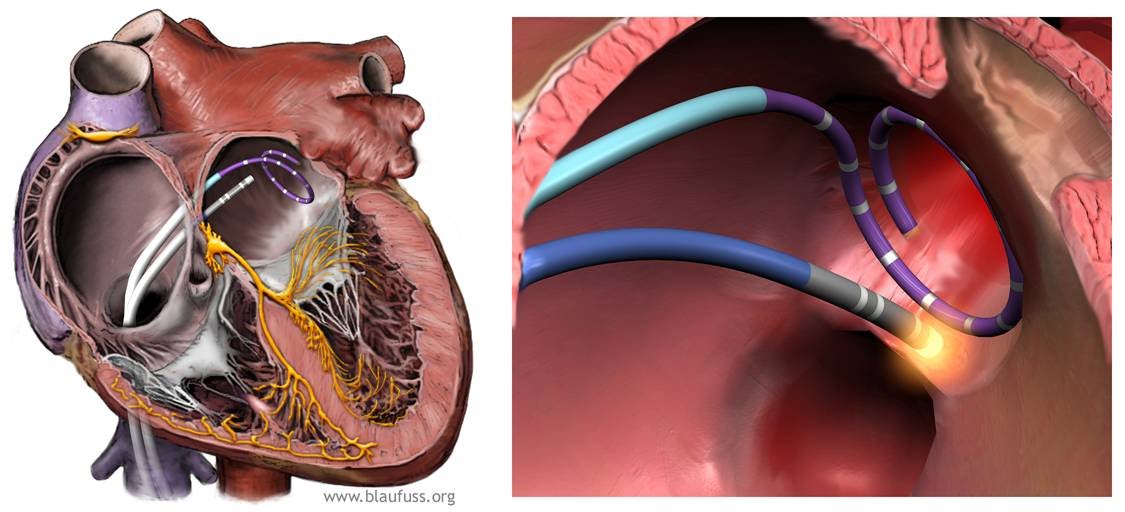
In the picture on the left you can see that two instruments (catheters) have been inserted into the left atrium. The round catheter is called a lasso catheter and is used as a measuring instrument to ensure that the isolation of the electrical impulses is perfect all the way around. In the picture to the right see the instrument that performs the ablation itself, a catheter that applies heat.
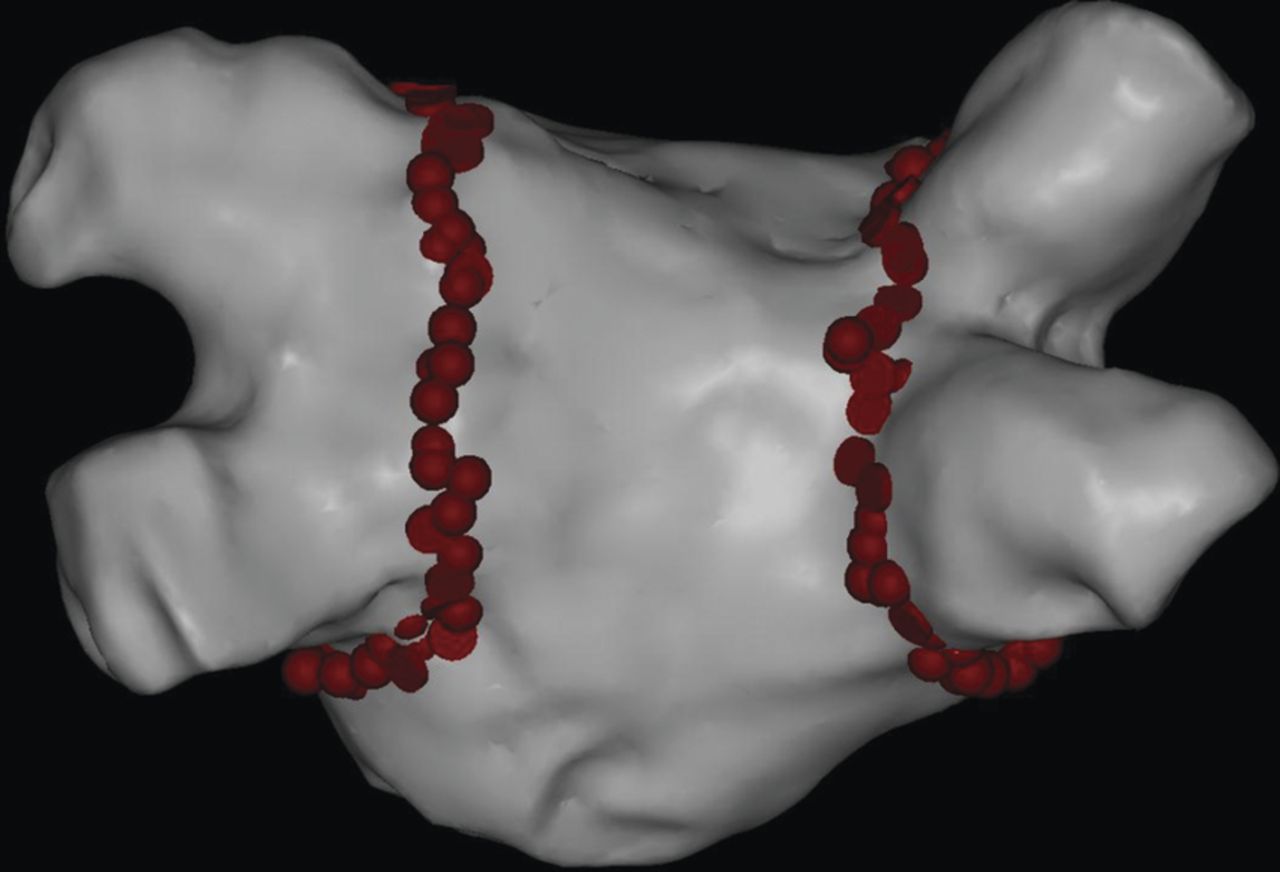
Advanced computer technology is often used for this type of treatment as in the figure above. Computer technology enables physicians to very accurately draw a three-dimensional model of the left atrium.
The red dots mark where ablation treatment was performed in order to create a barrier to electrical impulses. This type of computer technique is necessary as you cannot see through blood, which renders the use of endoscopical techniques impossible.
It is also possible to use low temperatures instead of high, this approach is called cryoablation. Both heating and cooling works well with high efficiency and low risk of side effects and complications. The preference of one technique or the other should be based on experience with either technique.
How effective is ablation treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Ablation is considered to be a very effective treatment for atrial fibrillation. This is especially true if the patient only has episodic atrial fibrillation. If atrial fibrillation is constantly present, then results are not quite as effective, depending on how long the atrial fibrillation has been constantly present..
Despite its efficacy, around 20% of patients will need to repeat the treatment. However, after this, 90% will no longer experience a recurrence of atrial fibrillation. This drops to 70% in the case of patients who have constant atrial fibrillation symptoms prior to treatment. This means that it is important to promptly seek care for atrial fibrillation to maximize your chances of a full recovery.
The risk of ablation treatment for atrial fibrillation
The treatment is not without risk. If performed improperly there can be bleeding from the heart into the surrounding areas of the body. There are also risks of blood clot complications, or the narrowing of the pulmonary vein openings. In very rare cases an incorrect connection can form between the esophagus and left atrium. However in trained hands the risk of complications during treatment are low and my own experience is that the overall risk of complications is significantly below 0.5%.
You will typically only need short lasting hospitalization for the procedure and return home the day after the treatment – sometimes even the same day. For the first one or two weeks, you will need to avoid activities that can strain the groin, where the treatment took place. This mostly concerns heavy lifting and sports activities, although light exercise should be okay.
After the treatment
It is also important to remember that in the first weeks after treatment, you can sometimes experience restless heart rhythm and atrial fibrillation. This doesn’t mean that the treatment has been unsuccessful, and these symptoms will typically fade. The reason for this is that the treatment itself causes stress on your heart.
This means that it is often advisable to continue any medication you were using to control your atrial fibrillation even for some time after your ablation treatment. After a few weeks, you should be able to end the course of your heart rhythm correcting medication. That being said, it is often recommended that patients continue to take blood-thinning medication.
1 comment